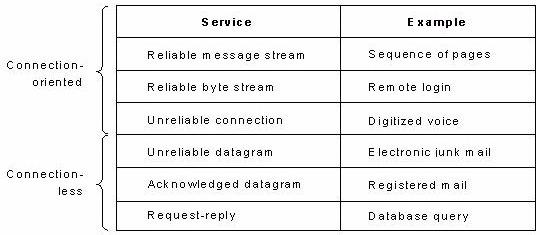
Computer network layers can offer two different types of services: Connection - Oriented and connection - less Service
Connection -oriented and connection less services through which one host can connect to another for exchanging their information. these are as follows.Connection-oriented service:
The service user first establishes a connection, uses the connection, and then releases the connection. Just like the telephone system.
It acts as a tube: the sender pushes objects (bits) in at one end, and the receiver takes them out in the same order at the other end. This method is often called a reliable network service. It can guarantee that data will arrive in the same order.
Reliable connection-oriented service has two minor variations: message sequences and byte streams. In the former, the message boundaries are preserved. In the latter, the connection is simply a stream of bytes, with no message boundaries.
For some applications, the delays introduced by acknowledgements. It is for telephone users to here a bit of noise on the line or a garbled word from time to time than to introduce a delay to wait for acknowledgements.Connection Less service:
A good analogy for a connectionless service is the process of sending letters just like the postal service. Each letter (message) carries the full destination address, and each one is routed through the system independent of all the others.
Unlike the connection-oriented service, when two messages are sent to the same destination, it is possible that the first one sent can be delayed so that the second one arrives first.
Unreliable (not acknowledged) connectionless service is called datagram service, which does not provide an acknowledgement back to the sender.
The acknowledged datagram service can be provided one short message that message is reliability to the sender.
Another service is the request-reply service. In this service the sender transmits a single datagram containing a request; the reply contains the answer.
 |
| Connection-Oriented and connection-less Service |
|
Fig. Six different types of services.
Well, how you found this article, is this useful? I'm sure this will help you more. If you want more information please let me know through comments in the right below.
Subscribed to the My Computer Tutors for updates. I will keep updating to you with latest tutorials.

Comments
Post a Comment
Your comment will inspire me, Please leave your comment